| News/Press Releases | ||
| Read more | ||
| Testimonial | ||||
|
||||
| Read more | ||||
| About Pancreas |
 |
| What is the pancreas? |
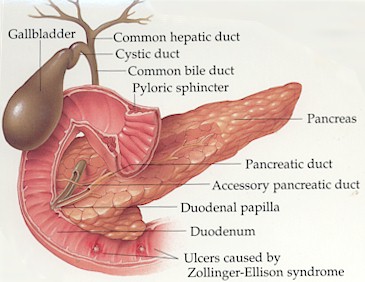
| pancreas[pankrEus] -The Greek name "pancreas", meaning "all flesh" or "all meat", is descriptive of the protein composition of this powerful organ which resembles a fish with a large head and a long tail. In actuality, the pancreas is an elongated, tapered organ located across the back of the abdomen, behind the stomach. This glandular organ secretes digestive enzymes and hormones. In humans, the pancreas is a yellowish organ about 7 in. (17.8 cm) long and 1.5 in. (3.8 cm) wide. The right side of the organ (called the head) is the widest part of the organ and lies in the curve of the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine. The tapered left side extends slightly upward (called the body of the pancreas) and ends near the spleen (called the tail). Inside, the organ's appearance resembles a stalk with clusters of grapes attached to it. The "stalk" is a long duct which runs down the center of the pancreas and the "grapes" are clusters of cells which flow into this duct and later into the duodenum for digestion of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. |
 |
| Parts of the Pancreas |
| There are 5 parts to the pancreas: uncinate process - The part of the gland that bends backwards and underneath the body of the pancreas. Two very important blood vessels, the superior mesenteric artery and vein cross in front of the uncinate process. head - The widest part of the gland. It is found in the right part of abdomen, nestled in the curve of the duodenum which forms an impression in the side of the gland. neck - The thin section between the head and the body of the gland. body - The middle part of gland between the neck and the tail. tail - The thin tip of gland in the left part of abdomen in close proximity with the spleen. |
| Purpose of the Pancreas |
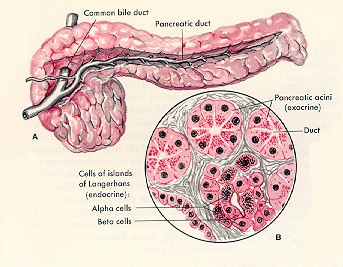
The pancreas has digestive and hormonal functions and is made up of two types of tissue: Exocrine TissueThe exocrine tissue consists of Acinar cells and pancreatic ducts. These are the exocrine (exo= outward) cells of the pancreas that produce and transport chemicals that will exit the body through the digestive system. The chemicals that the exocrine cells produce are called enzymes. They are proteins secreted in the duodenum where they assist in the digestion of food. Endocrine TissueThe endocrine tissue consists of cell clusters known as islets of Langerhans. These endocrine (endo= within) cells of the pancreas produce and secrete hormones into the bloodstream. The main pancreatic hormones, insulin and glucagon, work together to maintain the proper level of sugar in the blood. The sugar, glucose, is used by the body for energy. Failure of the insulin-secreting cells to function properly results in diabetes, which can occur in two major forms, juvenile onset (Type 1) and adult onset (Type II). |